Vapes
E-cigarettes – How Do They Work and How Have Products Evolved?
E-cigarettes – How Do They Work and How Have Products Evolved?
Today, e-cigarettes are a common alternative to traditional tobacco smoking, but what exactly are these devices made of and how do different models differ? In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the anatomy of e-cigarettes, how they function, and the rapid evolution of products on the market.
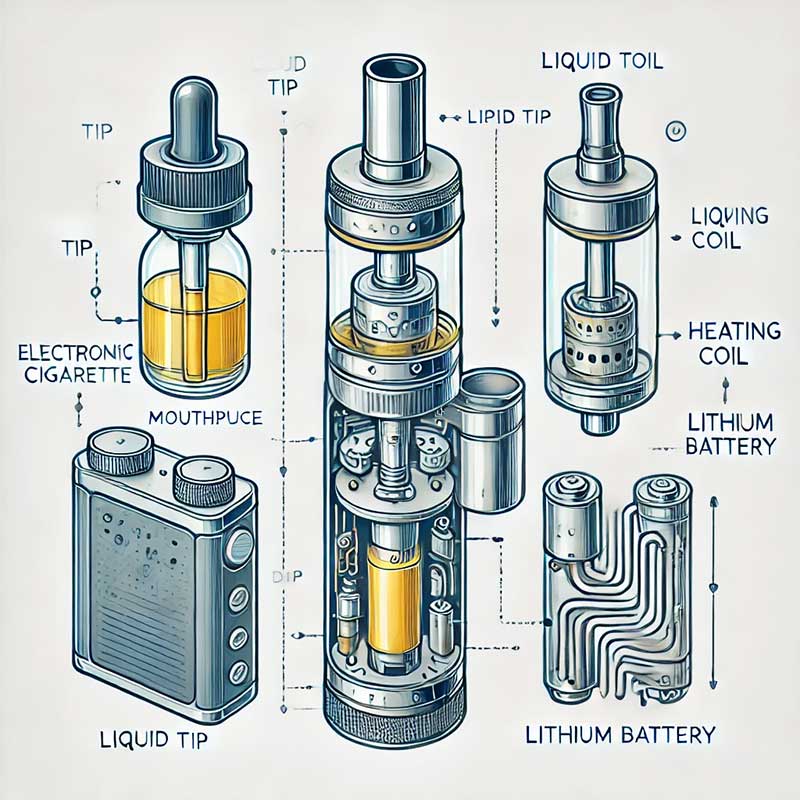
What Components Make Up an E-cigarette?
A typical e-cigarette consists of four main parts:
Mouthpiece (also known as a drip tip), where the user inhales the vapor.
Container for e-liquid (tank or cartridge).
Vaporizer with heating element (coil/atomizer) that converts liquid into aerosol.
Lithium battery, which provides power to the heating element.
When the user takes a puff, the battery activates, heating a metal coil wrapped around cotton or another absorbent material (the wick). The liquid is drawn up through the wick, heated, and transformed into an aerosol that is inhaled.
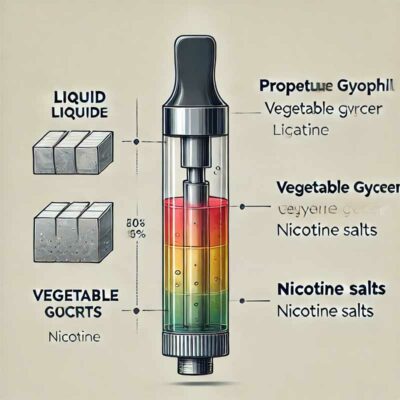
What Does E-liquid Contain?
E-liquid, also called e-juice, typically consists of:
Propylene Glycol (PG)
Vegetable Glycerin (VG)
Flavorings
Nicotine or synthetic nicotine-like substances (metatin)
PG and VG form the base of the e-liquid, carrying the flavorings and nicotine. PG provides a stronger throat hit, while VG produces more vapor. The exact composition affects user experience and where aerosol particles deposit in the respiratory system.
Types of Nicotine – Freebase vs. Nicotine Salts
Traditionally, e-liquids contained primarily freebase nicotine, but today nicotine salts are more common. Nicotine salts are less irritating to the throat, allowing higher concentrations of nicotine with smoother inhalation. Additionally, nicotine salts are absorbed faster into the body, helping users more efficiently satisfy nicotine cravings.

Different Types of E-cigarettes – From Simple Disposables to Advanced Mods
The product development of e-cigarettes has rapidly evolved since their introduction in 2004, typically categorized into four generations:
1st Generation – Cig-a-likes
These resemble traditional cigarettes and come in disposable or refillable models. However, they have low battery capacity and limited performance.
2nd Generation – Pen-style Models
Pen-shaped e-cigarettes with larger batteries and transparent tanks clearly showing the liquid. These are usually refillable, offering better vapor production compared to cig-a-likes.
3rd Generation – Mods & Sub-ohm Systems
More advanced and larger models allowing users to control power, resistance, and temperature, customizing vapor production and flavor experience.
4th Generation – Pod Systems
Highly popular among both new and experienced users, pod systems use pre-filled or refillable pods, often containing nicotine salts and featuring a compact, discreet design.
Pod Systems – Practical and Popular Alternatives
Pod systems have gained popularity due to their convenience and ease of use. With a fixed rechargeable battery and interchangeable pods, users don’t need to discard the entire device when the liquid runs out, saving money and reducing waste. Available pod sizes typically range from around 2ml up to refill bottles of 10ml, offering flexibility.
Safety and Potential Health Risks
Although e-cigarettes do not contain tobacco or produce the same level of harmful substances as traditional cigarettes, regular use carries certain health risks, especially for non-smokers. Primarily, nicotine is addictive and poses health risks, particularly for pregnant individuals and those with cardiovascular conditions.
For smokers transitioning from cigarettes, switching to e-cigarettes can reduce health risks, as many harmful substances produced by burning tobacco are either absent or present at significantly lower levels in e-cigarettes.
Environmental Concerns – From Disposables to Sustainable Solutions
Disposable models with built-in batteries have been criticized for environmental impact, often improperly discarded containing lithium batteries. Pod systems with reusable batteries offer a more sustainable alternative, and some manufacturers, like Vozol, use partly recycled materials.
Regulation and the Future of E-cigarettes
Regulation of e-cigarettes varies greatly between countries, significantly influencing future product development. Flavor bans and nicotine strength limits have been implemented in some regions to reduce usage among youth, while other regions allow greater flexibility to promote e-cigarettes as alternatives to smoking.
Future developments may include advanced features such as smart devices with Bluetooth and AI, personalized e-liquids, and greater focus on environmentally friendly solutions.
Summary
E-cigarettes provide an alternative to traditional tobacco smoking, continually evolving with rapid product development. Recent trends indicate increased popularity of practical pod systems, improved nicotine formulations such as nicotine salts, and a clear shift towards sustainable options. As the market grows and regulations evolve, staying informed about these developments is increasingly important.